Speeches Shim
Photo by Karen Kasmauski/MCSP
295,000 MOTHERS &
5.3M CHILDREN DIE GLOBALLY EACH YEAR
including over 2.5M newborns who die in their first month and almost 1 million on their first day of life.
Learn more about how USAID supports nurses and midwives with the skills for success.
A MESSAGE FROM USAID LEADERSHIP
BY THE NUMBERS
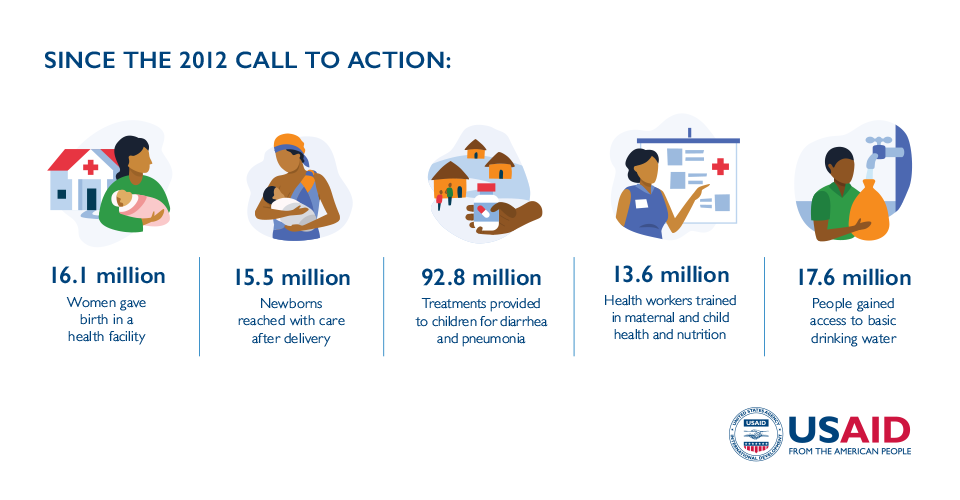 -->
-->
OUR APPROACH
 MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH
MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH
Mothers and children play invaluable roles in families, communities, societies, and economies. One million children are left motherless each year, and these children are then less likely to survive childhood.
In the past ten years, USAID has helped save the lives of more than 9.3 million children and 340,000 women.
Learn MorePhoto by Kate Holt for JHPIEGO/MCSP
 FAMILY PLANNING
FAMILY PLANNING
An estimated 214 million women want to delay or stop childbearing but can’t access contraception. Satisfying the global unmet need for family planning could reduce maternal deaths by 30 percent.
In our priority countries, the percent of demand for family planning satisfied by a modern method has increased from 46% in 2012 to 53% in 2017.
Learn MorePhoto byKate Holt for Jhpiego/MCSP
 MALARIA
MALARIA
Approximately 125 million pregnant women annually are at risk of contracting malaria. USAID-supported malaria interventions are implemented to reduce maternal and child mortality.
In countries supported by the U.S. President’s Malaria Initiative (PMI), nationwide surveys show significant declines in mortality rates among children under five, up to 67%.
Learn MorePhoto by Kate Holt/MCSP and Jhpiego
 NUTRITION
NUTRITION
Malnutrition is an underlying cause of an estimated 45% of child deaths and anemia contributes to 20% of maternal mortality. USAID supports country-owned programs that address the root causes of malnutrition to save the lives of women and children and lay the foundation for healthier futures.
Over the past 10 years, the prevalence of child stunting has decreased from 40% to 32.8% across 19 USAID-supported countries.
Learn MorePhoto by Spring Project/USAID
 WATER, SANITATION & HYGIENE
WATER, SANITATION & HYGIENE
Investments in water, sanitation and hygiene empower women, increase productivity and promote gender equality. Every $1 spent on improving sanitation results in an estimated $5 of economic gain.
In the past decade, USAID’s water activities have helped more than 27.2 million people have gained access to an improved sanitation service.
Learn MorePhoto by Allan Gichigi/MCSP
STORIES
Photo: USAID Systems for Health
EQUIPPING HEALTH PROVIDERS WITH THE KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS TO IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF CARE IN GHANA
Many rural clinics around the world lack funding to train staff on quality service delivery. In Ghana, USAID provided a multi-pronged approach to improve the quality of maternal and child health care, including building a primary care provider network to serve as a platform to support knowledge exchange between providers, build staff skills, and encourage wider adherence to quality standards of care.
Read MorePhoto: Sukriti Gangola/USAID VRIDDHI Project
AMERICAN INGENUITY IMPROVES PNEUMONIA DETECTION AND TREATMENT IN INDIA
Meet Mumtaz Bano, a community health officer at a Health and Wellness Center in the Mewat district of India, who works to improve newborn and child health by helping families to identify and treat infectious diseases. In partnership with Masimo, a U.S.-based manufacturer, USAID has introduced an innovative multimodal pulse oximeter in 19 health centers to help health workers like Mumtaz better diagnose pneumonia.
Read MorePhoto: Oscar Siagian/ USAID JALIN Project
PARTNERING WITH CONVENIENCE STORES TO BRING HEALTH SERVICES CLOSER TO HOME IN INDONESIA
When Ibu Asnah was pregnant with her third child, giving birth in a health facility did not cross her mind, and she was not aware of the risks of at-home deliveries, especially for high-risk pregnancies. USAID has partnered with Alfamart, a nationwide convenience store chain in Indonesia, to support health corners where midwives hold free counseling sessions for women like Asnhan, to educate them on maternal health, including understanding the symptoms of high-risk pregnancies and accessing health facilities for delivery.
Read MorePhoto: Sanele Nkomani, Feed the Future Innovation Lab for Nutrition
DIETITIANS ARE BLAZING THE WAY FOR IMPROVED NUTRITION PRACTICES IN MALAWI
Dietitians have been historically absent from Malawi’s health workforce, despite a pressing need for them, especially in intensive care units to monitor the nutrition status of critically ill patients. In partnership with Malawian and U.S.-based academic institutions, USAID helped develop the country’s first postgraduate dietetics degree program. In just a short period of time, these registered dietitians are already changing the clinical nutrition practice environment in Malawi for patients and healthcare teams.
Read MorePhoto: Pathfinder International
IMPROVING ACCESS TO CARE TO ADVANCE MATERNAL HEALTH OUTCOMES IN NIGERIA
Meet Cynthia John, a young woman living in Ogoja, Nigeria. Her rural community is far from the nearest health facility, so when she found out she was pregnant with triplets, she was concerned about being able to reach the facility in time to deliver her children safely. Through a partnership with Merck for Mothers, USAID is supporting emergency transport services in rural Nigeria to increase access to essential maternal health services and empowering women like Cynthia to seek care.
Read MorePhoto: MCSP
BUILDING THE FUTURE OF TANZANIA’S HEALTH WORKFORCE
Living in rural Tanzania, Modesta Morris had always wanted to be a nurse to help women have a healthy, positive pregnancy experience and combat Tanzania’s high rates of maternal and child mortality. A USAID-supported training program made Modesta’s dreams a reality, enabling her to graduate with a nursing and midwifery diploma and start her career as a nurse. Now, more nurses and midwives like Modesta are able to provide comprehensive, quality health care to women, children, and families across the country.
Read MorePhoto: Dorothy Nabatanzi/ Uganda Sanitation for Health Activity
SUPPORTING LOCALLY-LED SANITATION INNOVATIONS IN UGANDA THROUGH NEW AND STRENGTHENED PARTNERSHIPS
Meet Mary, a community health worker in Uganda that fights to prevent diarrhea in her community. After receiving a USAID- and private-sector-led training on innovative sanitation products, Mary began selling these locally-manufactured toilets door-to-door in her community and working with local masons to correctly install them, improving her communities’ access to safe sanitation and building a business to support herself in the process.
Read MoreCOUNTRY UPDATES
- SELECT A COUNTRY
- Afghanistan
- Bangladesh
- Burma
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Ethiopia
- Ghana
- Haiti
- India
- Indonesia
- Kenya
- Liberia
- Madagascar
- Mali
- Malawi
- Mozambique
- Nepal
- Nigeria
- Pakistan
- Rwanda
- Senegal
- South Sudan
- Tanzania
- Uganda
- Yemen
- Zambia
Click on a country: USAID's efforts in maternal and child survival focus on 25 priority countries that account for more than 66% of global maternal and child deaths.
Afghanistan
Provided 3,478 women with Sayana-Press, a novel injectable that can be easily self-administered or administered by community health workers and pharmacists every three months under the skin to avoid unintended pregnancies
Bangladesh
Piloted a new approach to reach the 50 percent of women who do not deliver in health facilities with community-level postpartum and post-abortion family planning care through utilizing frontline health workers and paid peer volunteers to deliver key messages
Burma
Supported maternal, neonatal, and child health training for clinicians and a new quality improvement model at one hospital in Rakhine State, which led to a 55 percent increase in infection prevention and 25 percent reduction in complications around labor and delivery in just two years
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Supported communities in nine provinces to revitalize nearly 2,300 sites for integrated community case management of childhood illness (iCCM) and retrained 170 community health workers on updated national protocols to deliver lifesaving iCCM services to hard-to-reach children
Ethiopia
Trained 631 nurses and midwives on respectful maternity care, increasing the number of facilities providing women-friendly health support
Ghana
Facilitated cross-facility collaborations between health workers to share experiences and skills, describe challenges to providing care, and identify solutions. These efforts contributed to a 33 percent reduction in institutional maternal mortality, 41 percent increase in family planning service utilization, and 28 percent reduction in stillbirths among participating districts in just a year and a half
Haiti
Developed a strategic plan for improving human resources for health in Haiti, including increasing country ownership through a plan for transitioning health workforce salary support from international organizations to the Government of Haiti, and as a result, 100 community health workers’ salaries were included in the domestic health budget for the first time this past year
India
Partnered with the private sector to train more than 85,000 new nurses to improve their employment prospects and reduce health worker shortages
Indonesia
Partnered with local private sector companies to develop maternal and newborn health corners within nation-wide convenience store chains that provide women with free counseling and check-ups with midwives
Kenya
Contracted more than 200 health workers across 11 of Kenya's 47 counties to provide maternal, newborn, child health, and nutrition counseling and care in facilities that were not functioning due to lack of skilled staff, and county governments are now working to transition at least 20 percent of these health workers to government payroll in the next year
Liberia
Updated the national pre-service curriculum for nurses and midwives, in collaboration with the Liberian Board for Nursing and Midwifery, to include training on the Essential Care for Every Baby and the Helping Babies Survive protocols
Madagascar
Trained 9,226 health volunteers across 34 districts on community plague surveillance and preparedness, including measures to support prevention, rapid detection and treatment for new cases, and comprehensive response to potential outbreaks
Mali
Coached more than 1,800 front line health providers, including nurses, midwives, and medical doctors, across 824 facilities on the provision of quality reproductive, maternal, newborn, and child health, voluntary family planning, and nutrition care
Malawi
Provided more than 1,100 nurses, clinicians, and other service providers from 869 health facilities and village clinics with training, mentorship, and supportive supervision to implement integrated community case management, a community-level approach to treat malaria, diarrhea, and pneumonia in children under five
Mozambique
Supported health facilities to improve the quality of maternal, newborn, and child health care through updating performance standards and providing training on quality improvement, resulting in 95 percent of supported health facilities improving their performance by at least 50 percent in the past year
Nepal
Trained 11,632 frontline health workers, including nurses, midwives, and community health workers, to provide integrated nutrition services across 42 targeted districts
Nigeria
Helped establish a community-led emergency transport system which made emergency obstetric and newborn care available and accessible within two hours for 92 percent of households in Cross River State
Pakistan
Supported 47 females and 34 males in a Master of Public Health degree program at Pakistan’s primary public health educational institution to build domestic health expertise and leadership
Rwanda
Provided competency-based on-the-job training and clinical mentorship to more than 2,400 medical providers, including certifying 330 providers as mentors to provide continued support and training to other health care workers
Senegal
Expanded a professional peer training program for public sector health workers to reach 75 private sector health providers across five major cities to improve the quality of care offered across all types of health facilities
South Sudan
Provided voluntary family planning care to more than 6,000 women through community outreach and health facilities in nine locations, which resulted in more than 1,200 family planning users taking up a wide range of contraceptives, including long-acting, short-acting, and fertility awareness methods
Tanzania
Supported quality improvement efforts in seven nursing and midwifery schools, which led to an 80 percent average improvement among graduates on midwifery competencies such as newborn resuscitation
Uganda
Provided capacity building training to 389 midwives across 143 private health facilities on basic emergency obstetric and newborn care, elimination of mother to child transmission of HIV/AIDS, and voluntary family planning, which led to 70 percent of the facilities scoring higher than 70 percent on the self-regulatory quality improvement system
Yemen
Zambia
Through a public-private partnership with a local bank that built a maternity waiting shelter, supported training for healthcare providers and community volunteers on skilled deliveries, increasing access to health care services for pregnant women in remote, hard-to-reach areas














Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.