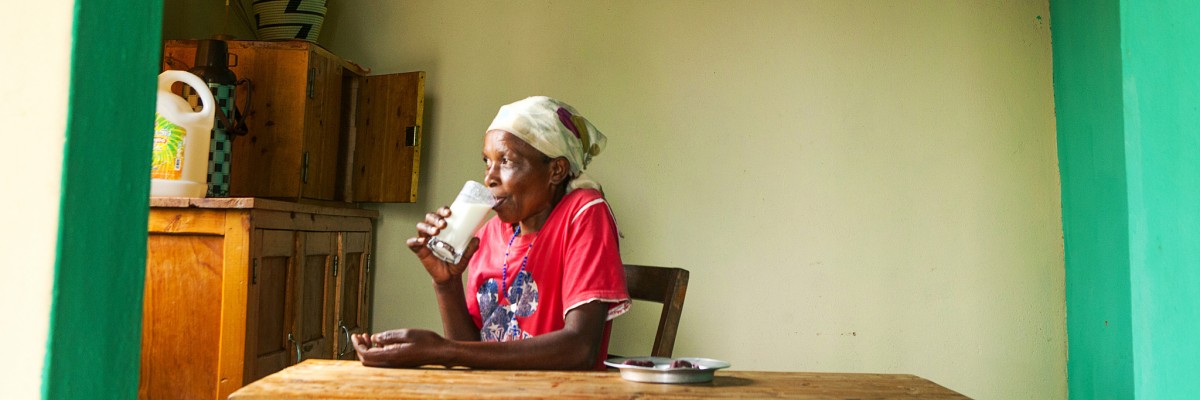
Rwanda is a small, landlocked country with the highest population density in Africa. It remains one of the world’s poorest countries. However, much has changed since the 1994 genocide. Today, the Government is committed to making it a middle-income country by 2020, a plan enshrined in its Vision 2020 plan. Data across sectors suggest the country is actively moving toward their goal. For example, between 2011 to 2014, poverty dropped markedly – from approximately 60 percent to 40 percent– and GDP per capita increased to approximately $750. This progress has been credited in large part to strong agriculture sector growth. Rwanda’s 2015 Demographic and Health Survey reported similar positive trends: between 1990 and 2015, the country reduced under-five child mortality rate by two-thirds and achieved an extraordinary 85 percent decline in maternal mortality. The survey also reports that 93 percent of children aged 12-23 months are fully vaccinated against major childhood diseases.
The country's progress is remarkable and USAID is working closely with the government, civil society, private sector and communities to build on this progress and address remaining challenges in health, economic growth, education and democracy and governance.





Comment
Make a general inquiry or suggest an improvement.